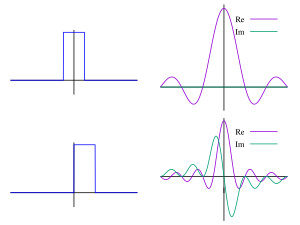
The Fourier Transform is a specialized form of the Laplace Transform. This being the case,
read about the Laplace Transform before reading about the Fourier Transform.
The Fourier Transform is defined:
There is also an inverse Fourier Transform, that transforms a function in the Fourier domain to a function in the time domain:
The Fourier Transform is a linear operation. There is also a discrete Fourier Transform formula:
and an inverse formula for the discrete time domain:
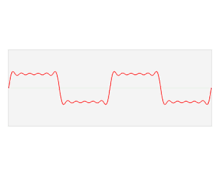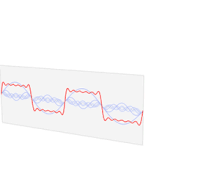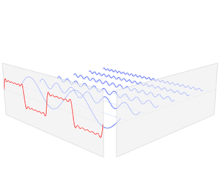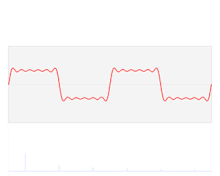
The Fourier Series is a sum of sinusoidal functions. This sum can be derived from a set of integers (Fourier Coefficients) that can be extracted from any function with a Fourier transform by evaluating the Fourier transform
at certain intervals. These integers can be used along with the fundamental frequency of the original time domain function to completely
reconstruct it from only the Fourier domain function. The Fourier coefficients are amplitudes of sinusoidal waves of integer multiples of the fundamental frequency,
which when summed together will form the original function. This means that every function can be represented as a sum of sinusoidal functions. However, for most
functions, this will be an infinite sum, so a reasonable approximation is required. This is as easy as using enough Fourier coefficients as necessary to make the approximation,
and truncating the further coefficients.